Line Spectrum of Gases.
Tungsten filament lamp (not clear in the photo due to the high brightness) emitting white light, mixture of all wavelengths, when seen through the grating glasses shows continuous spectrum VIBGYOR.
In the middle mercury vapour lamp is there which gives the line spectra, with few of the wavelengths.
In the top we have sodium vapour lamp, which gives the line spectra of almost just one wavelength. yellow, monochromatic 589.6 nm.
Line spectrum (sometimes also referred as finger prints of gases) which baffled scientists for a long time was later explained by Bohr's atomic model.
What is Continuous Spectrum and Line Spectrum?
What is Emission Spectrum and Absorption Spectrum?
Click on the gas name to change to Hydrogen, Helium, Neon, Mecury and Sodium Lines
Finger Prints of Gas
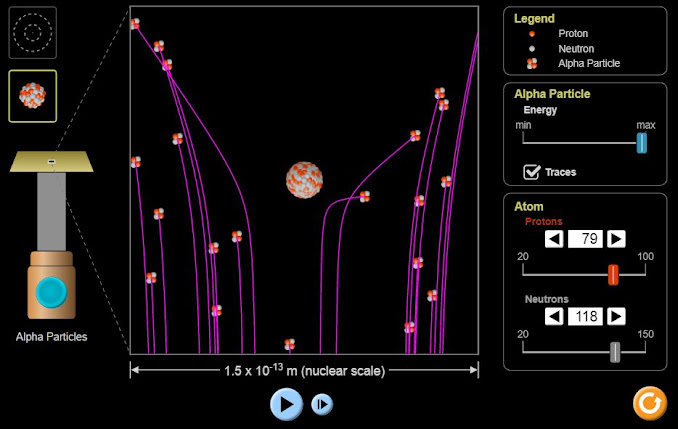
Rutherford, Geiger and Marsden's Alpha particle scattering experiment
with Thomson's Plum Pudding model and Rutherford's Nucleus model.
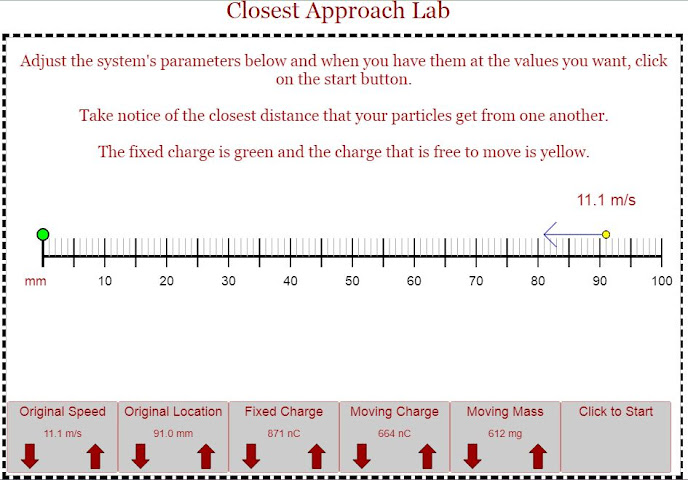
For the given numbers above find out the distance of closest approach, meaning how close will the charged particle reach to the fixed charge?
Try it with different values to check if your answer agrees with the simulation result.
Hint: Total Energy at starting point = Total energy at returning point
KE + PE = KE + PE
1/2 m v^2 + k q1 q2 / r = 0 + k q1 q2 / ro
ro is the distance of closest approach that needs to be found. Sol: 55 mm
Distance of Closest Approach: Estimation of Nucleus size.
Electrons are particles or waves?
Standing waves or stationary waves of electrons in Hydrogen atom.
Try different energy levels in Bohr's orbits and the corresponding waves of electrons.
Bohr's Quantization Condition from de Broglie's Wavelength
Observe the energy level transitions from one energy level to another and the corresponding EM waves emitted or absorbed.
Visit 11P14 Waves chapter page to learn about standing waves.
View different models of Hydrogen atom
Thomson's Plum pudding model, Classical Solar model, Bohr's quantized model,
de Broglie's electron wave model etc.
Estimate the energy of the photon, the frequency and wavelength of the EM wave that will be emitted from the energy level transition E2 to E1 and compare it with the simulation result.
Balmer-Rydberg Equation:
Hydrogen Spectrum: Lymann, Balmer, Paschen, Brackett, Pfund series:
Wavelength calculation using Balmer's equation:
Bohr's Formula Summary:
Velocity, Radius, Time Period, Frequency, Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy, Total Energy, Balmer's Empirical Formula, de Broglie wavelength of orbiting electron:
No. of possible transitions from higher to lower energy levels:
Limitations of Bohr's model:
Ionization Energy and Ionization Potential:
Typical Problems with Hydrogen atom colliding with Helium ions:
Hydrogen atom colliding with another stationary hydrogen atom:
Robert Millikan's Oil drop experiment to determine the elementary charge e = 1.6 x 10-19C:
What is Velocity Selector Arrangement?
Adjust the Magnetic Field and Electric Field (by changing the voltage) to make the electrons go undeflected?
Thomson's Cathode Ray Experiment to determine Specific Charge,
Specific Charge by Magnetic Field only,
Specific Charge by Electric Field only:
e/m = 1.7 x 1011 C kg-1
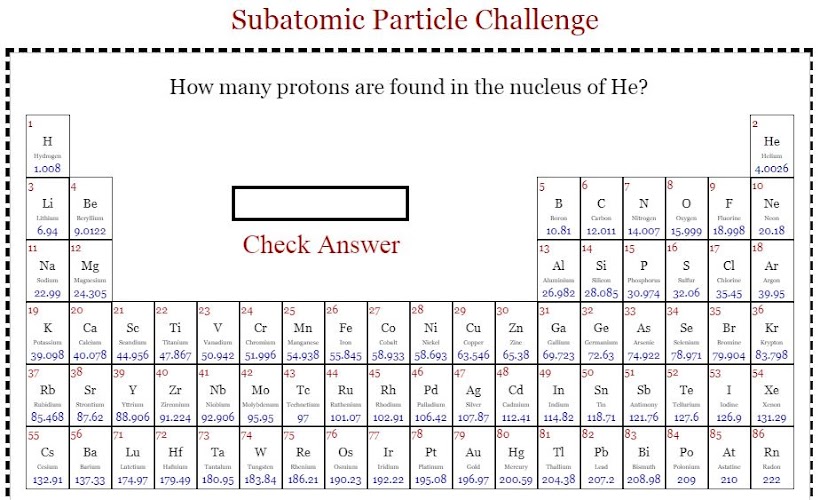
Take a simple quiz using Periodic table on Elements for their no. of protons, electrons and neutrons.
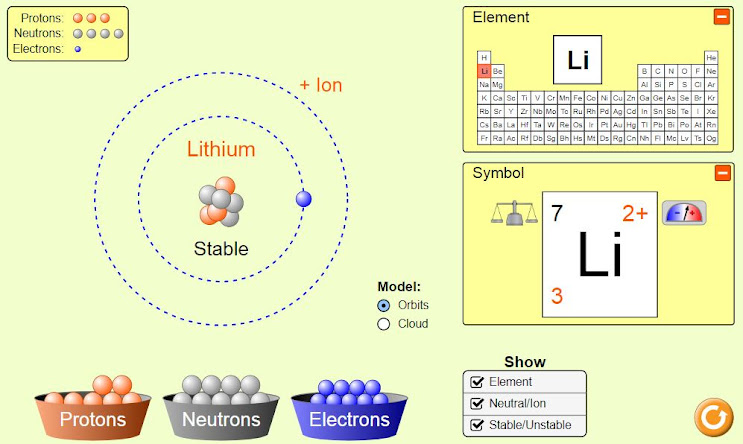
What are Hydrogenic atoms or Hydrogen like species? Identify them and build them from protons, neutrons and electrons.
X-ray Production: Coolidge tube:
X-ray Continuous Spectrum and Characteristic spectrum: Moseley's law:









No comments:
Post a Comment
Please provide your valuable feedback. Students, Parents, Teachers.