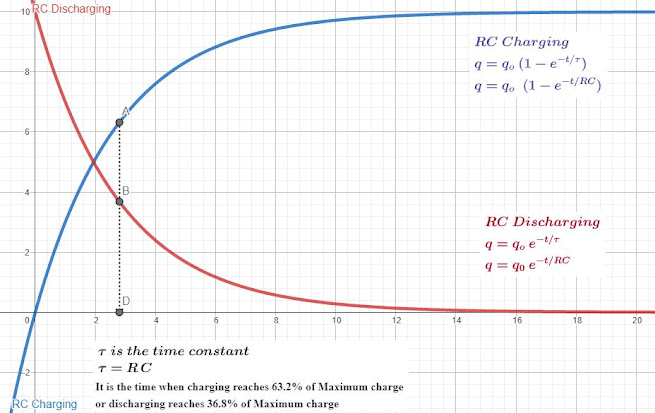
12P07B RL RC Charging Discharging Transient Currents
Preeti reached the metro station and found that the escalator was not working. She walked up the stationary escalator in time t1. On other days, if she remains stationary on the moving escalator. then the escalator takes her up in time t2. The time taken by her to walk up on the moving escalator will be:
Problem 7. Preeti reached the metro station and found that the escalator was not working. She walked up the stationary escalator in time t1. On other days, if she remains stationary on the moving escalator. then the escalator takes her up in time t2. The time taken by her to walk up on the moving escalator will be: [NEET 2017]
(a) t1t2
t2−t1
(b) t1t2
t2+t1
(c) t1 − t2
(d) t1+t2
2
A particle covers half of its total distance with speed $v_1$ and the rest half distance with speed $v_2$. Its average speed during the complete journey is
Problem 6. A particle covers half of its total distance with speed $v_1$ and the rest half distance with speed $v_2$. Its average speed during the complete journey is [NEET 2011M]
(a) $\frac {v_1 v_2}{v_1 + v_2}$
(b) $\frac {2 v_1 v_2}{v_1 + v_2}$
(c) $\frac {2 v_1^2 v_2^2}{v_1^2 + v_2^2}$
(d) $\frac {v_1 + v_2}{2}$
\[Avg. Speed = \frac {Total \; distance}{Total \; time}\]
\[ = \frac {\frac{d}{2} + \frac {d}{2}}{\frac{d/2}{v_1}+\frac{d/2}{v_2}}\]
\[=\frac{2 v_1 v_2}{v_1+v_2}\]
A car moves from X to Y with a uniform speed $v_u$ and returns to Y with a uniform speed $v_d$. The average speed for this round trip is
Problem 5. A car moves from X to Y with a uniform speed $v_u$ and returns to Y with a uniform speed $v_d$. The average speed for this round trip is [NEET 2007]
(a) $\sqrt{v_u v_d}$
(b) $\frac{v_d v_u}{v_d + v_u}$
(c) $\frac{v_d + v_u}{2}$
(d) $\frac{2 v_d v_u}{v_d + v_u}$
If a car at rest accelerates uniformly to a speed of 144 km/h in 20 s, it covers a distance of
Problem 4. If a car at rest accelerates uniformly to a speed of 144 km/h in 20 s, it covers a distance of [NEET 1997]
(a) 2880 m
(b) 1440 m
(c) 400 m
(d) 20 m
A bus travelling the first one third distance at a speed of 10 km/h, the next one third at 20 km/ h and the last one-third at 60 km/h. The average speed of the bus is
(a) 9 km/h
(b) 16 km/h
(c) 18 km/h
(d) 48 km/h
A car moves a distance of 200 m. It covers the first half of the distance at speed 40 km/h and the second half of distance at speed v. The average speed is 48 km/h. Find the value of v
Problem 2. A car moves a distance of 200 m. It covers the first half of the distance at speed 40 km/h and the second half of distance at speed v. The average speed is 48 km/h. Find the value of v [NEET 1991]
(a) 56 km/h
(b) 60 km/h
(c) 50 km/h
(d) 48 km/h
A car covers the first half of the distance between two places at 40 km/h and other half at 60 km/h. The average speed of the car is [NEET 1990]
Problem 1. A car covers the first half of the distance between two places at 40 km/h and other half at 60 km/h. The average speed of the car is [NEET 1990]
(a) 40 km/h
(b) 48 km/h
(c) 50 km/h
(d) 60 km/h
The magnitudes of vectors A, B and C are 3,4 and 5 units respectively. If A + B = C , then the angle between A and B is
NEET 1988
The magnitudes of vectors $\vec{A}, \vec{B} \; and \; \vec{C} $ are 3,4 and 5 units respectively. If $\vec{A} + \vec{B} = \vec{C}$ , then the angle between $\vec{A} \; and \; \vec{B}$ is
Pythagoras triplet $3^2 + 4^2 = 5^2$
So the angle will be $90^o$ between $\vec{A} \; and \; \vec{B}$
Coulomb’s law for electrostatic force between two point charges and Newton’s law for gravitational force between two stationary point masses, both have inverse-square dependence on the distance between the charges and masses respectively. (a) Compare the strength of these forces by determining the ratio of their magnitudes (i) for an electron and a proton and (ii) for two protons. (b) Estimate the accelerations of electron and proton due to the electrical force of their mutual attraction when they are 1 Å (= $10^{-10}$ m) apart? ($m_p$ = 1.67 × $10^{–27}$ kg, $m_e$ = 9.11 × $10^{–31}$ kg)
If $10^9$ electrons move out of a body to another body every second, how much time is required to get a total charge of 1 C on the other body?
How much positive and negative charge is there in a cup of water?
NCERT Example 1.2 How much positive and negative charge is there in a cup of water?
Home



Quick Links in this Website:
11P03 Motion in a Plane 2D
Circular Motion